Back-to-back receptacle
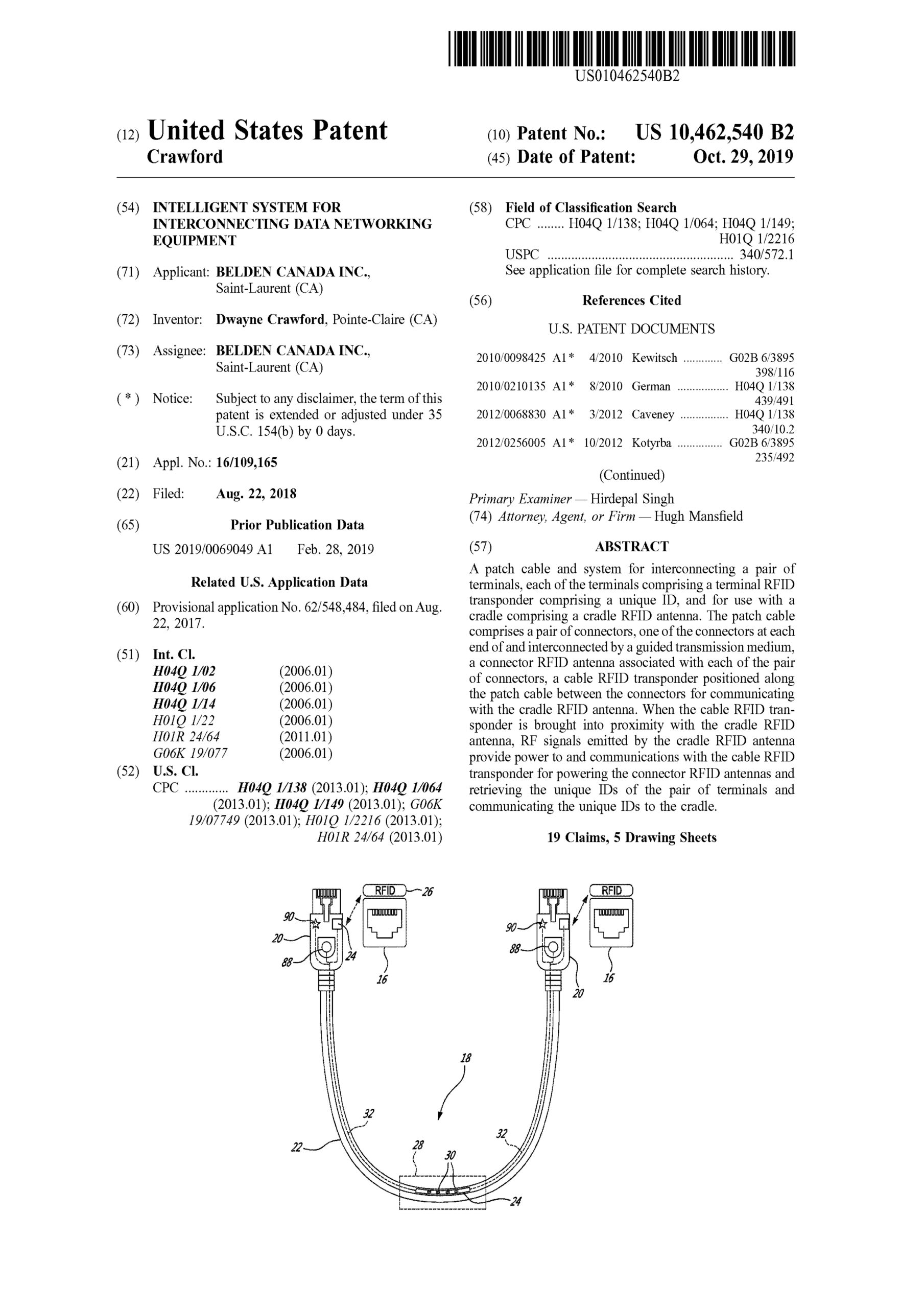
A back-to-back receptacle and system for providing selective interconnection between a pair of optic fibres. The system comprises a receptacle comprising a pair of back-to-back receptacle sockets, with at least a first of the sockets configured to one of a plurality of predefined receptacle keying geometries, a first connector plug terminating the first optic fibre, the plug adapted for insertion into the first receptacle socket, the plug configured to one of a plurality of predefined connector keying geometries and a second connector plug terminating the second optic fibre, the plug adapted for insertion into a second of the back-to-back receptacle sockets. At least one of the predefined connector keying geometries matches at least one of the predefined receptacle keying geometries. When the receptacle keying geometry of the first receptacle socket corresponds to the connector keying geometry of the first plug and optionally the receptacle geometry of the second of the back-to-back receptacle sockets corresponds to the connector keying geometry of the second plug, the first plug can be inserted in the first socket and the second plug can be inserted in the second socket bringing the first optic fibre into axial alignment with the second optic fibre.